Biomes Of The Earth Map
Written by: Karla Moeller
Illustrated by: Sabine Deviche
What'southward a Biome?

Here we see ii unlike biomes—deserts on the left and grasslands on the right. Only both are country environments. Images by Bob Protus and Bkell.
To brand sense of complexity, humans often need to categorize, or grouping, things. We have food groups, sexes, middle colors, ages, and movie genres, to name a few. We categorize all types of things, whether they are ideas or objects, and whether they are small-scale or large. 1 of the largest things that nosotros effort to categorize may be the types of environments institute on Earth.
The natural globe is more than varied than we can imagine, and one way to try to make this variation easier to handle is to put different environment types into groups. Nosotros can dissever our environs many ways—by how much water in that location is, by how warm it is, or by the types of plants or animals we detect at that place. Depending on what characteristics we choose to describe an environment, the groupings we end upward selecting may be unlike.
Usually we group the different natural areas on World into categories based on plant and animal life and how they are able to survive in that office of the world. Making groups based on living organisms can exist very complicated. Nosotros already know of over 1.7 million species of organism, and at that place are likely over 17 million that exist. But again, by grouping organisms with like adaptations together, nosotros can see through some of the complexity and take a chance to better empathize the living Globe.
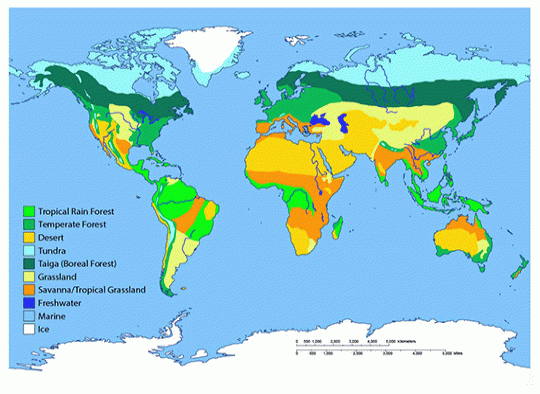
This biome map shows both land (terrestrial) and water (aquatic) based habitat types. Click for more than detail.
A biome is a type of environment that is divers past the types of organisms that live there. We can likewise think of these as life zones ("bio" ways life). Dividing land up in this way lets us talk about areas that are similar, fifty-fifty if they're on different continents. Merely depending on whom you talk to, the way we carve up up the world into separate biomes differs.
Biome vs. Biome
Biome categories can be broad or narrow. When we say forest, you may picture a absurd, placidity expanse with pine copse, where bears, deer, and rabbits wander effectually. Or instead, you might imagine a wet, dark, and noisy rainforest, where y'all can see monkeys, parrots, and big cats.

These are all types of forests, but some people split them into different woods-blazon biomes. Click to meet more detail.
According to some people, all wood types vest in one grouping – the forest biome. Just others remember that temperate forests (seasonally cold) with pine trees, are very different from tropical rainforests, with dense, leafy awning and lots of rain. This divergence of stance means that the number of biomes can range anywhere from 5 to 20 biomes.
How Different is Different?
Temperate forests get a winter flavour, often with snowfall. Tropical rain forests are also warm to get snow. Image by Böhringer.
If we take a closer wait at these temperate and pelting forests, nosotros see that they differ quite a bit in the amount of rain they get and in their temperatures. Tropical rainforests are warm and don't experience a winter season. But temperate forests have a defined winter, with snowfall and temperatures below null.
With those cold temperatures, the plants and animals in temperate rainforests have to have adaptations to deal with cold weather. Do those groups seem different enough to yous to be in a separate biome?
Don't worry, there is no right or incorrect answer. This method of categorizing is 1 of convenience, and sometimes it just depends on why you're dividing the groups.
Biomes of the World
In order to give y'all a small taste of the huge diverseness of the types of environments out there, we carve up the world up into only ix biomes. Simply remember that these groups could as well be divided into nearly twenty biomes. That ways that within each of these biomes in that location is a range of temperature and weather condition conditions, and nosotros as well find some organisms that are adapted to only role of the biome and others that are adapted to the full range of conditions inside the boundaries we are defining.
Tropical Rainforest

Tropical rainforest. Image by WorldWideHappyMedia
You probably picture tropical rainforest as a jungle, where information technology stays warm all year. There are as well many animals to count and the huge numbers of trees go along their leaves year-round. Many of these forests become so much rain that there isn't even much of a dry season – more similar a rainy flavor and a rainier season.
Temperate Forest

Temperate forest. Epitome past Umberto Salvagnin.
This is the kind of wood where in that location are four relatively distinct seasons. Many of the copse shed their leaves in the fall and become inactive through the cold winter. In these forests, you lot find deer, woodpeckers, and bears, some of which hibernate through the winter.
Desert

A desert with sand dunes. Paradigm by Jon Sullivan.
Deserts make upwardly the hottest biome, only tin also get cold temperatures in wintertime. Such temperature swings make this an extreme environment, where many animals take to couch surreptitious to find more stable temperatures in order to survive. Plants and animals here must be able to withstand long periods without h2o.
Tundra

Tundra in Greenland. Prototype by Hannes Grobe.
Tundra is flat and cold with low plants like grass and moss that only grow during the short summer. A thick layer of ice lies just below the shallow soil (permafrost) all year around, and copse cannot penetrate it to ballast their roots. Many birds visit the tundra in the summer to nest, merely most escape the wintertime by migrating to warmer areas. Mice and other small mammals stay active during the winter in protected tunnels under the snow.
Taiga (Boreal Forest)

Boreal forest of Alaska. Image by L.B. Brubaker.
Taiga is the largest land (terrestrial) biome in the world. Information technology is fabricated upwardly of mainly conical-shaped evergreen trees with needle-similar leaves. These trees are called conifers considering their seeds are clumped into cones. The taiga has long, common cold winters when about mammals hibernate and birds migrate, or leave the surface area considering the winters are too cold for them to stay. Animals like weasels, bickering and rabbits that do not drift or hibernate grow dense feathers or fur and plough white to match the snow.
Grassland

Grasslands. Paradigm by Tony Hisgett
Sometimes chosen plains or prairie, grasslands are near entirely short to tall grasses with no trees. This land type gets just enough pelting to help grasses, flowers, and herbs abound, just stays dry enough that fires are frequent and trees cannot survive. Here we find large mammals that often travel together in huge herds.
Savanna

Savanna in Tanzania. Image by Nevit Dilmen.
These tree-studded grasslands receive enough seasonal rainfall so that trees tin can grow in open up groups or singly throughout. The animals living hither have long legs for escaping predators and usually are seen in herds. A combination of fire and grazing animals are important for maintaining the savannah.
Freshwater

Lakes are usually freshwater, like this lake in Pakistan. Image past Joonasl.
This water biome is named for the low concentration of table salt found in the water. This includes near ponds, streams, lakes, and rivers. Because salt is important to body office, the plants and animals here have many adaptations that assistance them save salt.
Marine

Marine environments have common salt water, like this tidepool in Portugal. Image past Alvesgaspar.
This water biome is the largest biome in the world, as it includes the v major oceans that cover 70% of the Earth. Marine water has high levels of common salt, then animals and plants living hither have adaptations that assistance them get rid of salt or take on h2o.
Virtual Biomes
Virtually visit some of the biomes without having to travel.
Take a virtual look within some of these biomes using a reckoner, smart telephone, tablet, or Google Goggles. Our first two virtual biomes are the desert and rainforest. Compare how the two are different and how they are the like. Write upwards your results in our biologist notebook.
Additional images from Wikimedia via Adrien Facélina and Pam Brophy.
Biomes Of The Earth Map,
Source: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/explore/biomes
Posted by: echevarriaentlets.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Biomes Of The Earth Map"
Post a Comment